 2차원 배열 길이 및 모양
2차원 배열 길이 및 모양
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2차원 배열
int [][] arrTwo = new int[3][2];
int num = 1;
/*
// arrTwo[0][0] = 1;
// arrTwo[0][1] = 2;
// 위의 내용을 아래처럼 for문으로 변경
for(int col = 0; col<2; col++, num++) {
arrTwo[0][col] = num;
}
// arrTwo[1][0] = 3;
// arrTwo[1][1] = 4;
// 위의 내용을 아래처럼 for문으로 변경
for(int col = 0; col<2; col++, num++) {
arrTwo[1][col] = num;
}
// arrTwo[2][0] = 5;
// arrTwo[2][1] = 6;
// 위의 내용을 아래처럼 for문으로 변경
for(int col = 0; col<2; col++, num++) {
arrTwo[2][col] = num;
}
*/
/* 위의 블록을 이중 for문으로
for(int row=0; row<3; row++)
for(int col = 0; col<2; col++, num++) {
arrTwo[row][col] = num;
}
*/
// 길이 상관없이 만들기
int rowLength = arrTwo.length; // 3
for(int row=0; row<rowLength; row++) {
int colLenght = arrTwo[row].length; // 2
for(int col = 0; col<colLenght; col++, num++) {
arrTwo[row][col] = num;
}
}
System.out.println(arrTwo); // 배열의 주소값이 출력됨
// 내용이 출력되는게 아니라 10000번지의 정보값만 출력됨
// 배열 내용 출력
for(int row=0; row<rowLength; row++) {
int colLenght = arrTwo[row].length; // 2
for(int col = 0; col<colLenght; col++) {
System.out.print(arrTwo[row][col] + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
 결과
결과
 문제 맨 처음 맨끝은 1 중간은 이전행+ 그 위의 값 합친 값 넣기
문제 맨 처음 맨끝은 1 중간은 이전행+ 그 위의 값 합친 값 넣기
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [][]arrTwo3; // 선언
arrTwo3 = new int[5][]; // 행 생성
// 행별 열 생성
// arrTwo3[0] = new int[1];
// arrTwo3[1] = new int[2];
// arrTwo3[2] = new int[3];
// arrTwo3[3] = new int[4];
// arrTwo3[4] = new int[5];
int rowLength = arrTwo3.length; //5
for(int i = 0; i<rowLength; i++) {
arrTwo3[i] = new int[i+1];
}
// arrTwo3[0][arrTwo3[0].length-1] = 1;
// arrTwo3[1][0] = 1;
// arrTwo3[1][arrTwo3[1].length-1] = 1;
// arrTwo3[2][0] = 1;
// arrTwo3[2][arrTwo3[2].length-1] = 1;
// arrTwo3[3][0] = 1;
// arrTwo3[3][arrTwo3[3].length-1] = 1;
// arrTwo3[4][0] = 1;
// arrTwo3[4][arrTwo3[4].length-1] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i<rowLength; i++) {
arrTwo3[i][0] = 1;
int colLength = arrTwo3[i].length;
for(int j = 1; j<colLength-1; j++) {
arrTwo3[i][j] = arrTwo3[i-1][j-1] + arrTwo3[i-1][j];
}
arrTwo3[i][colLength-1] = 1;
}
for(int[]valueArr : arrTwo3) {
for(int value: valueArr) {
System.out.print(value +",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
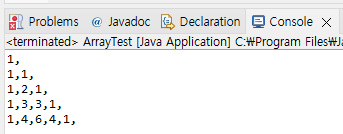 결과
결과
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String []subject = {"국어", "수학", "영어"}; // 과목
int subjectLength = subject.length; //3
int [][]arrTwo4 = new int[10][subjectLength]; // 최대 10명의 학생점수(국어, 수학, 영어)
// arrTwo4[0][0]=10; //1번 학생의 국어점수 10점
// arrTwo4[0][1]=5; //1번 학생의 수학점수 5점
// arrTwo4[0][2]=7; //1번 학생의 영어점수 7점
java.util.Scanner sc = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int no = 0; // 학번
while(no < 10) {
// 학생수가 11인 경우에는 반복을 빠져나오기
// if(no == 0) {
// break;
// }
System.out.print("점수입력을 진행하시겠습니까[y/n]");
String yn = sc.next();
if(yn.equals("n")) {
break;
}
// System.out.print((no+1) + "번 학생의 국어점수:");
// int k = sc.nextInt();
// arrTwo4[no][0] = k;
//
// System.out.print((no+1) + "번 학생의 수학점수:");
// int m = sc.nextInt();
// arrTwo4[no][1] = m;
//
// System.out.print((no+1) + "번 학생의 영어점수:");
// int e = sc.nextInt();
// arrTwo4[no][2] = e;
// 위의 3블럭 for문으로
for(int i = 0; i < subjectLength; i++) {
System.out.print((no+1) + "번 학생의 " + subject[i] + "점수:");
arrTwo4[no][i] = sc.nextInt();
}
no++;
}
//학생들의 점수를 출력하기
//1번 학생점수: 국어- , 수학-, 영어-
//2번 학생점수: 국어- , 수학-, 영어-
//국어과목 평균:
//수학과목 평균:
//영어과목 평균:
int []totalScoreSubject = new int[subjectLength];//과목별 총점
System.out.println("학생들의 점수를 출력하기");
for(int i = 0; i < no; i++) {
System.out.println((i+1) + "번 학생점수:");
int totalScore = 0; //학생별 총점
for(int j =0; j<subjectLength; j++) {
totalScore += arrTwo4[i][j];
}
//System.out.println("국어-" + k + ", 수학-" + m + ", 영어-" + e);
for(int j = 0; j < subjectLength; j++) {
System.out.print(subject[j] + "-");
System.out.print(arrTwo4[i][j]);
}
System.out.println(", 총점-" + totalScore + ", 평균-" + (float)totalScore/3);
//과목별 총점 누적하기
for(int j = 0; j < subjectLength; j++) {
totalScoreSubject[j] += arrTwo4[i][j];
}
}
for(int j = 0; j < subjectLength; j++) {
System.out.println(subject[j] + "과목 평균 :" + (float)totalScoreSubject[j]/no);
}
}
}
 결과
결과






